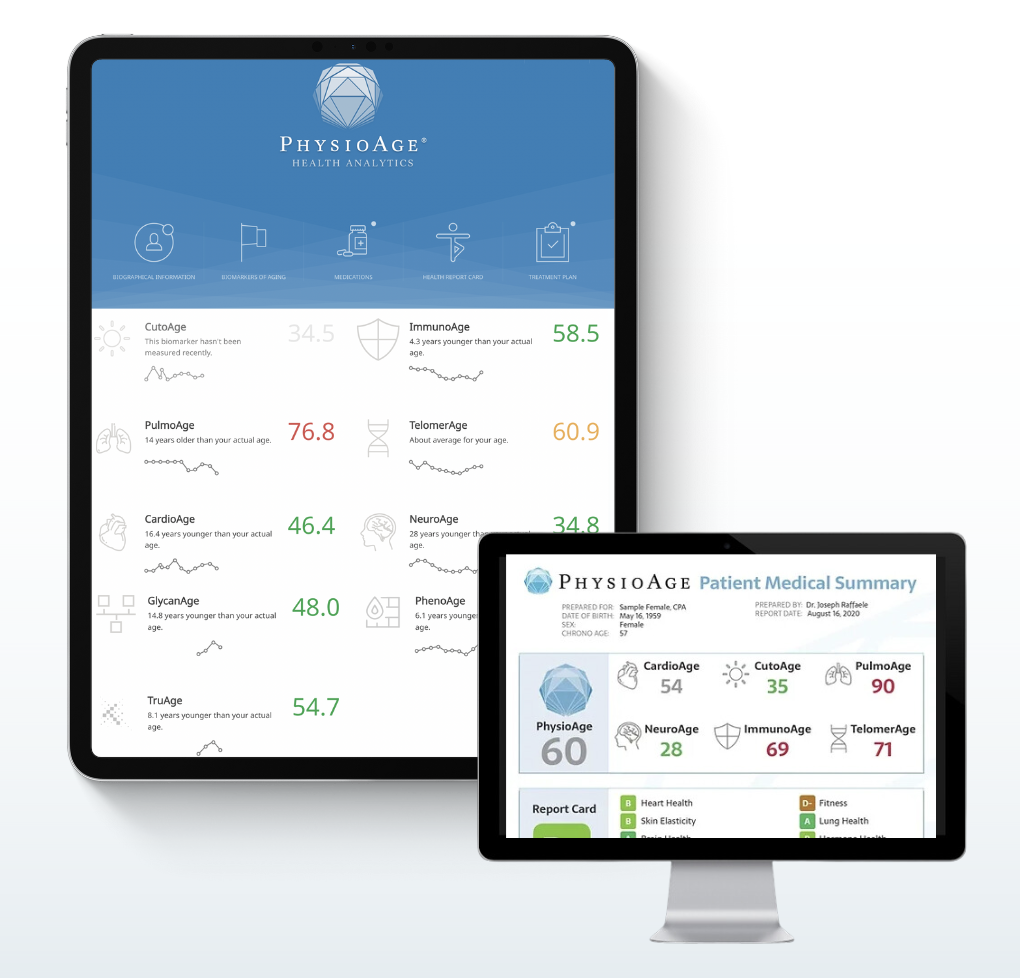
- Measures intrinsic aging based on age-related methylation changes to the DNA governed by genetics and heritable epigenetic changes.
- Measures extrinsic aging based on the decline in immune function corresponding with age-related decline of tissue performance and disease risk.
- Includes the Dunedin Pace of Aging measure to assess years of biological aging per year
- Measures biological aging based on organ system function using nine biomarkers found in routine blood tests that are influenced by lifestyle genetic factors.
- Correlates highly with chronological age and predicts all-cause mortality and death from specific diseases and can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of therapies.
- Evaluates the pattern of sugar molecules (glycosylation) covering immunoglobulins and functions as a marker of hormone optimization treatment response.
- Characteristic patterns are strongly associated with age, disease states, and unhealthy lifestyles.
- Measures the ends of the telomeres, the caps at the ends of your chromosomes that act as a molecular clock by shortening with every cell division
- Telomere shortening is highly correlated in numerous studies with aging and many disease states
- Measures the health of the immune system using proprietary algorithms of standard immune subsets
- Utilizes cutting-edge molecular markers for senescent and naïve T-cells
- Measures the suppleness of your arteries using pulse wave analysis
- Assesses cardiovascular risk by measuring augmentation pressure
- Measures forced expiratory volume (FEV1/FCV), which is highly correlated with age
- Predicts all-cause mortality, not just mortality from pulmonary disease
- Measures the most highly age-sensitive aspects of cognitive function using a computerized battery of tests
- Functions as an effective screen for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease